[ad_1]
Breaking Down the Elements of MACD
The MACD sometimes consists of three parts. The MACD line represents the 12-day Exponential Transferring Common (EMA) subtracted from the 26-day EMA. The second aspect is the sign line, which is the 9-day EMA of the MACD. The ultimate part is the MACD histogram, indicating the disparity between the MACD line and the sign line.
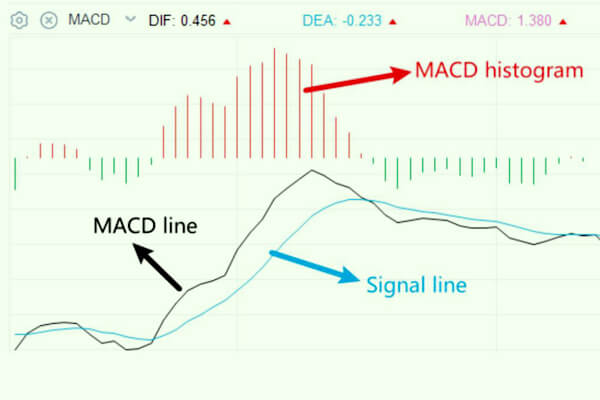
However, the parameters of the MACD line also can modify based mostly on the merchants’ desire. To distinguish these parts clearly, DIF constantly denotes the MACD line, whereas DEA all the time signifies the sign line.
The elemental idea of the MACD line is that the shorter-term EMA represents current worth motion, whereas the longer-term one signifies previous exercise. Subsequently, if there’s a vital hole between these two EMAs, the market is both trending upward or downward. Moreover, the MACD histogram, which fluctuates round a zero line, denotes the vigor of the development.
Evaluation of MACD Alerts
Crossovers
The intersections of the MACD line and the sign line can recommend a shift in worth development. Some illustrations are offered within the upcoming graphs.A optimistic sign is acknowledged when the MACD line strikes from beneath to above its sign line.
A bullish sign happens when the MACD line strikes up and crosses above the sign line.
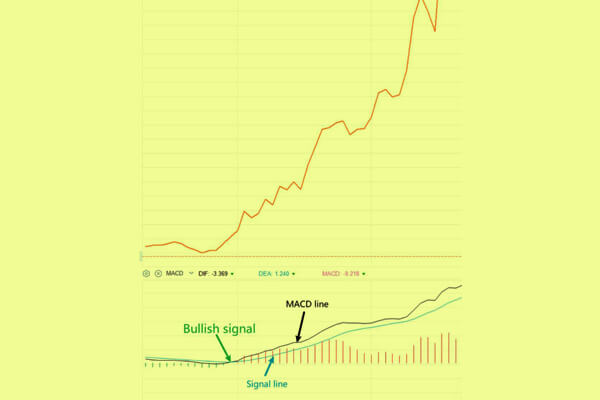
A bearish sign happens when the MACD line strikes downward, crossing under the sign line after being above it.
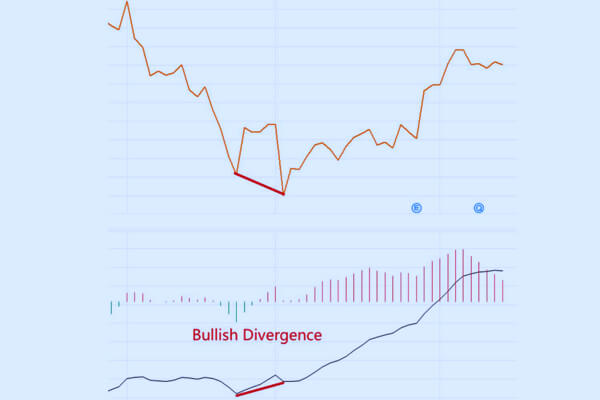
Divergence is displayed when the MACD line and the worth exhibit contrasting tendencies. The divergence sign could recommend a possible shift in a development. For example, if the MACD line is transferring upward whereas the worth varieties a decrease low, a bullish divergence takes place, indicating that the worth motion could develop into optimistic.
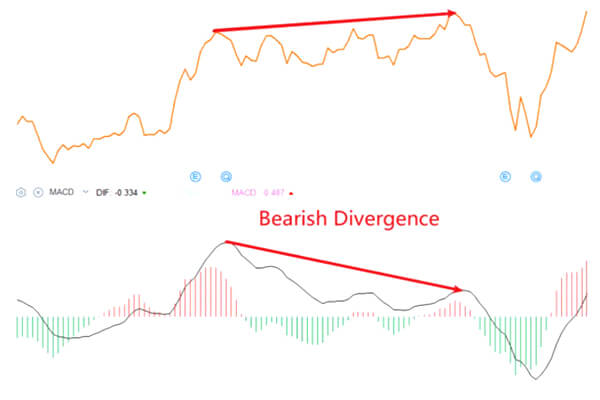
Alternatively, if the MACD line is transferring downward whereas the worth reaches the next excessive, a bearish divergence emerges, suggesting that the worth motion could develop into adverse.
Zero-Cross Technique
When the MACD crosses from beneath to above the zero line, it’s considered a bullish indication. Merchants sometimes provoke lengthy positions when this occurs. Conversely, if it crosses from above to under the zero line, it’s seen as a bearish sign by merchants. On this case, merchants enter quick positions to capitalize on declining costs and rising downward momentum.
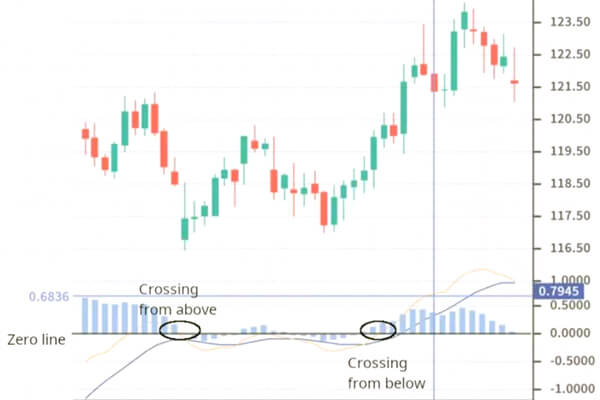
In each situations, the longer the histogram bars, the stronger the sign. When a robust sign is current, it’s extra possible—however not assured—that the worth will persist within the trending route.
Disadvantages of MACD
Like every oscillator or indicator, the MACD has limitations and hazards.
Reversal Sign
Ineffectiveness of MACD in lateral markets
MACD doesn’t carry out successfully in lateral markets. When costs predominantly oscillate sideways inside a spread outlined by help and resistance, MACD typically shifts towards the zero line as a result of absence of an upward or downward development—the place the transferring common is best.
Lagging Alerts
Moreover, the MACD zero-cross acts as a lagging indicator because the worth sometimes stays above the prior low earlier than the MACD crosses the road from beneath. This can lead to coming into an extended place later than you probably might have.
[ad_2]




